Unlock the Secrets to Perfect Solar Inverter Installation: Indoor vs. Outdoor Revealed!
As the world increasingly turns to renewable energy sources, the importance of proper solar inverter installation cannot be overstated. A solar inverter is a critical component of any solar energy system, converting the direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) that can power your home. However, the effectiveness of this technology hinges significantly on where you choose to install your inverter. This article will delve into the essential considerations for both indoor and outdoor installations, providing insights that can enhance your energy efficiency and prolong the lifespan of your system. Understanding the right placement not only assures optimal functionality but also minimizes maintenance issues, making it a wise investment for any homeowner looking to harness solar energy.
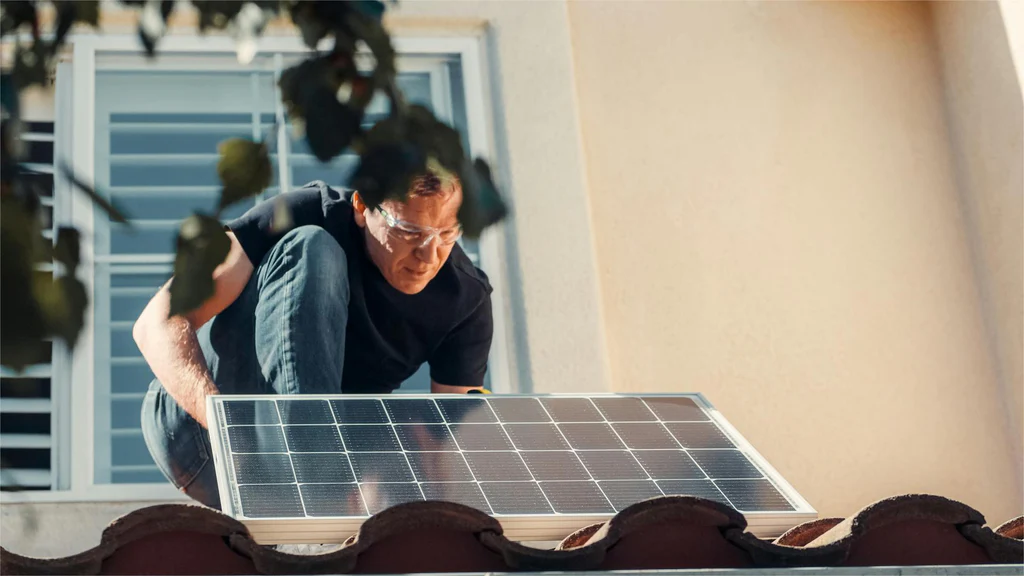

Understanding Solar Inverters
A solar inverter is often referred to as the brain of a solar energy system. Its primary role is to convert the DC electricity generated by solar panels into AC electricity, which is used in homes and businesses. There are several types of inverters available, including string inverters, microinverters, and power optimizers, each with its unique advantages and applications. For instance, string inverters are typically more cost-effective for larger systems, while microinverters offer better performance in shaded environments. Understanding the type of inverter that best suits your solar setup is crucial for maximizing the efficacy of your investment.
Indoor Installation Considerations
Installing a solar inverter indoors comes with several advantages. Primarily, it protects the inverter from harsh weather conditions, which can lead to wear and tear over time. Indoor installations also enhance security, as the inverter is less susceptible to theft or vandalism. However, there are several key factors to consider when opting for an indoor installation. Adequate space is necessary to accommodate the inverter and any additional equipment, such as batteries. Ventilation is critical as well; without proper airflow, the inverter can overheat, reducing its efficiency and lifespan. Additionally, the proximity to the solar panels is important; shorter wiring runs can minimize energy loss. A friend of mine, who recently installed a solar system, shared how they transformed a small utility room into an inverter space, ensuring proper ventilation and accessibility for future maintenance.
Ventilation Needs
Proper ventilation is paramount for indoor installations to prevent overheating. Inverters generate heat during operation, and without adequate airflow, they can reach critical temperatures that affect performance. To achieve proper ventilation, consider installing the inverter in a location that allows for air circulation, such as a room with windows or vents. If necessary, supplemental ventilation systems or fans can be installed to enhance airflow, especially in smaller spaces.
Accessibility for Maintenance
Easy access to the inverter is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting. When selecting a location, ensure that the inverter is positioned where it can be reached without difficulty. Regular maintenance checks can prevent potential issues from escalating and prolong the lifespan of the inverter. My neighbor learned this the hard way; they installed their inverter in a cramped attic and found it challenging to perform routine checks.
Outdoor Installation Considerations
Outdoor installation of a solar inverter can offer unique benefits, such as reduced heat build-up, which can be advantageous in maintaining optimal operating temperatures. Additionally, outdoor installations may provide easier access to sunlight, which can be especially beneficial for energy efficiency. However, environmental factors such as weather conditions and potential exposure to the elements are critical considerations. Inverters installed outdoors need to be carefully protected from rain, snow, and extreme temperatures to ensure reliable performance. A friend who installed their inverter outdoors mentioned that they initially underestimated the importance of proper placement, leading to some challenges during the rainy season.
Weatherproofing and Protection
To protect an outdoor inverter from environmental damage, weatherproofing is essential. This can involve installing the inverter in a weather-resistant enclosure or using protective covers specifically designed for outdoor use. Additionally, consider the location of the inverter; placing it under an overhang or in a shaded area can help shield it from direct exposure to rain and sunlight, ultimately enhancing its durability.
Location and Sunlight Exposure
Choosing the optimal location for outdoor inverter installation is crucial for maximizing sunlight exposure. Ideally, the inverter should be placed in an area that receives ample sunlight throughout the day while avoiding shading from nearby trees, buildings, or other structures. Proper positioning ensures that the inverter operates efficiently, contributing to the overall performance of the solar energy system.
Comparative Analysis: Indoor vs. Outdoor
When deciding between indoor and outdoor installations, it’s helpful to weigh the pros and cons of each. Here’s a quick comparative analysis:
- Indoor Installation Pros: Protection from weather, enhanced security, less risk of environmental damage.
- Indoor Installation Cons: Requires adequate space and ventilation, may increase maintenance challenges.
- Outdoor Installation Pros: Reduced heat build-up, easier access to sunlight, potentially simpler installation.
- Outdoor Installation Cons: Vulnerable to weather conditions, requires weatherproofing and protection measures.
Key Considerations for Inverter Installation
Choosing the right location for your solar inverter is a crucial decision that can significantly impact the efficiency and longevity of your solar energy system. Whether you opt for an indoor or outdoor installation, understanding the unique considerations and best practices associated with each option is essential. As you assess your specific situation, consider factors such as ventilation, accessibility, weatherproofing, and sunlight exposure. Making an informed choice will not only enhance your energy efficiency but also ensure that your investment in solar energy pays off in the long run.