Unlock the Power of the Sun: Your Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Perfect Solar Inverter!
As the world increasingly shifts towards sustainable energy sources, the importance of solar energy cannot be overstated. Solar inverters play a crucial role in harnessing this renewable resource, converting the direct current (DC) electricity produced by solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity suitable for home use. Selecting the right solar inverter can significantly impact your energy efficiency and savings, especially when looking for specific features like a 3000w 24v solar inverter with overload protection. Understanding these features is essential for effective energy management and ensuring your solar system operates optimally.
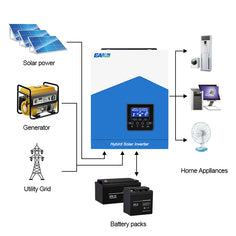
Understanding Solar Inverters
A solar inverter is the heart of a solar energy system, responsible for converting the DC electricity generated by solar panels into AC electricity. There are several types of solar inverters available on the market, each with its unique benefits and drawbacks. String inverters, the most common type, connect multiple solar panels in series, making them a cost-effective choice for many homeowners. Microinverters, on the other hand, are installed on each individual solar panel, providing improved efficiency and performance, particularly in shaded conditions. Lastly, hybrid inverters combine features of both string and microinverters, allowing for battery storage integration and grid-tied systems. Each type serves a different purpose, and understanding these distinctions is crucial when selecting the right inverter for your solar setup.
Key Features of Solar Inverters
When purchasing a solar inverter, several essential features should be taken into consideration. Efficiency ratings are paramount, as they indicate how well the inverter converts energy and minimizes losses. Installation requirements can vary significantly between models, so it's important to assess whether your space can accommodate the chosen inverter type. Warranty terms also play a vital role in ensuring protection against potential issues down the line. Specifically, the 3000w 24v solar inverter with overload protection stands out due to its ability to handle excess load, preventing damage to both the inverter and connected appliances. This feature is especially important in regions with fluctuating power demands, providing peace of mind that your system remains safe and reliable.
Benefits of Overload Protection
Overload protection is a critical feature in solar inverters that prevents the system from exceeding its maximum power capacity. When too much electricity flows through the inverter, this protective mechanism kicks in, either by disconnecting the load or limiting the output. The advantages of having overload protection are significant; it safeguards the entire system from damage, extends the lifespan of both the inverter and connected devices, and ensures safe operation during peak usage times. For instance, a friend of mine had invested in a solar inverter without this feature and experienced frequent power outages during heavy usage periods. In contrast, those who opted for models with overload protection found their systems running efficiently and without interruptions.
Choosing the Right Solar Inverter for Your Needs
Assessing your energy needs is the first step in choosing the right solar inverter. Calculate your household's total energy consumption and match it with the inverter's specifications. Key considerations include power capacity, which should ideally exceed your peak usage to accommodate unexpected surges. Compatibility with solar panels is another crucial factor; ensure that the inverter can handle the voltage and current produced by your solar array. Additionally, professional installation is highly recommended to guarantee safety and optimize performance. A well-installed inverter can significantly enhance the efficiency and reliability of your entire solar system, providing you with the best return on your investment.
Common Misconceptions About Solar Inverters
There are several misconceptions surrounding solar inverters that can deter potential buyers. One common myth is that inverters require extensive maintenance; however, most modern inverters are designed to be low-maintenance and only need periodic checks. Another misconception is that solar inverters are inefficient, but advancements in technology have led to highly efficient models capable of converting over 95% of the energy produced. Additionally, some believe environmental conditions negatively impact inverter performance; in reality, many inverters are built to withstand various weather conditions and can operate effectively even in less-than-ideal environments. Addressing these myths can help potential buyers feel more confident in their solar investment.
Maximizing Your Solar Investment
In summary, selecting the right solar inverter is crucial for maximizing the benefits of your solar energy system. The 3000w 24v model with overload protection offers an excellent balance of power capacity and safety features, ensuring your system operates efficiently while safeguarding your investment. As you embark on your journey toward sustainable energy, take the time to conduct thorough research and consult with professionals to make an informed decision that suits your specific needs. With the right solar inverter, you can unlock the full potential of solar energy and enjoy its many benefits for years to come.



